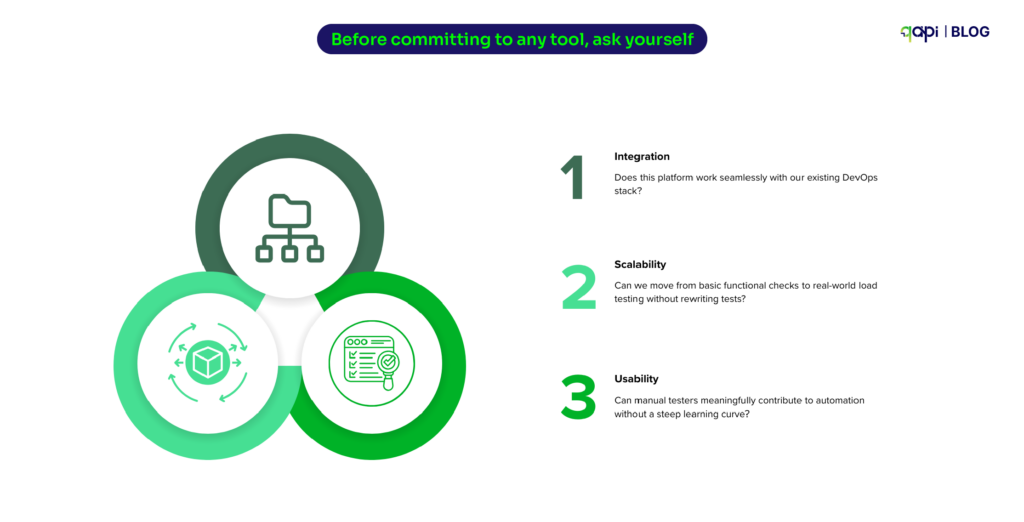
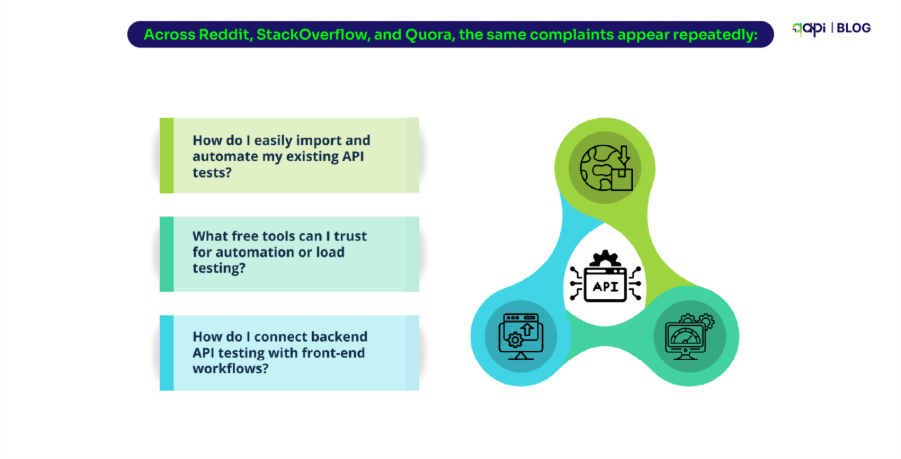
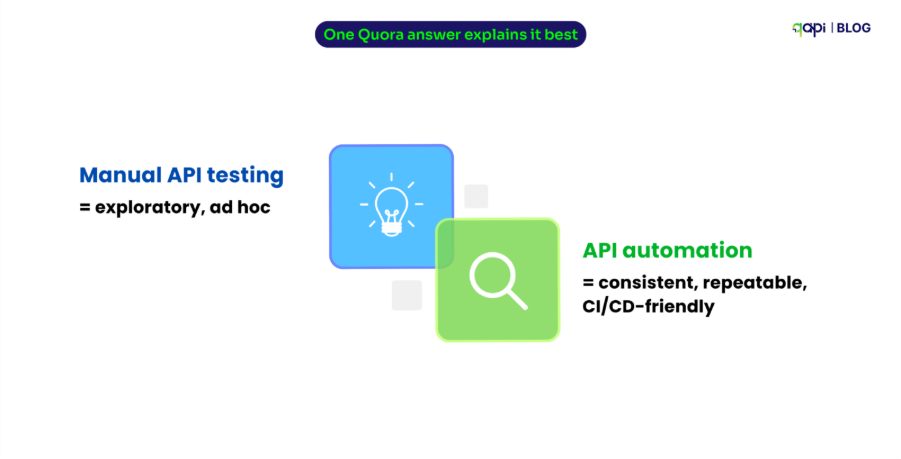
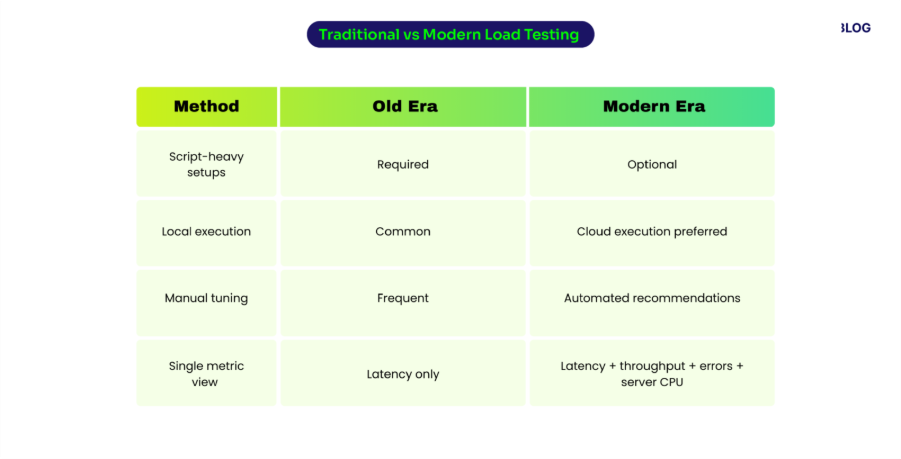
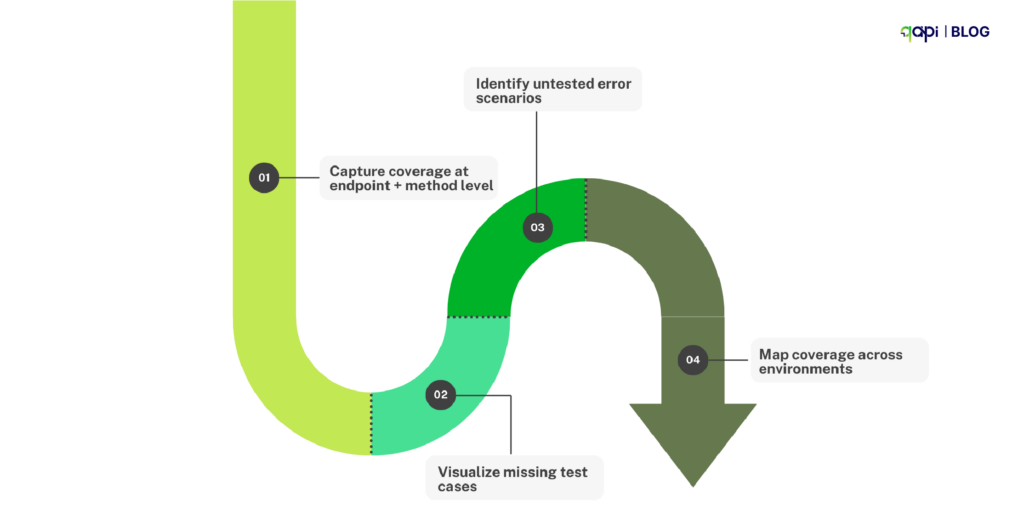
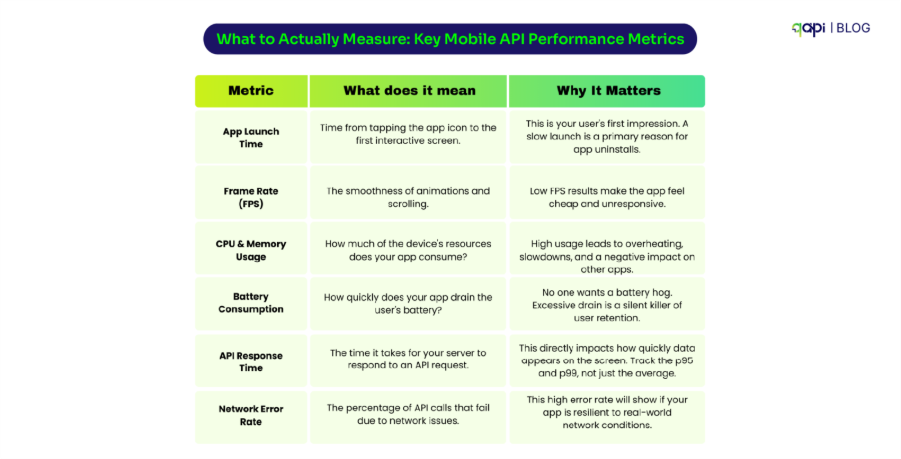
When someone asks “How would you scale a REST API to serve 10,000 requests?”, they’re really asking how to keep the API fast, reliable, and affordable under heavy load.
This question comes up because REST APIs—especially in Node.js—are easy to build but harder to scale. Everything works fine with 10 requests per second, but as you try to scale to 10,000+ requests per second, your setups will show all the red flags.
This tutorial will walk you through the most practical, repeatable and effective ways to handle REST APIs on qAPI that will help you improve your API testing lifecycle.
“Scaling a REST API to handle tens of thousands of requests per second is less about chasing a specific number and more about building the right foundations early. “
What we see across multiple APIs don’t fail because of bad logic; they fail because they were designed for today’s traffic, but not tested tomorrow’s growth.
REST APIs dominate because they’re simple enough for beginners yet powerful enough for Netflix-scale systems. While GraphQL, SOAP, and RPC have their strengths, REST hits the sweet spot of simplicity, tooling support, and developer familiarity that makes it the default choice for 70% of modern APIs.
So let’s see how teams should actually handle them.
What should teams do?
Step 1:The first principle is understanding what your application server is actually good at.
Event-driven servers are designed to handle large numbers of concurrent connections efficiently, but the only catch is that they have to be used correctly.
They excel at I/O-heavy workloads, such as handling HTTP requests, calling databases, or talking to other services. Problems begin when CPU-heavy or blocking operations are introduced into request paths.
When that happens, concurrency drops sharply and latency increases rapidly. The lesson here is simple: keep request handling lightweight and push heavy computation out of the critical path.
Step 2: Next, plan for horizontal scaling from day one.
What I mean is instead of relying on a single powerful server, you should build your own system so multiple identical instances can serve traffic in parallel. This will help to add capacity gradually and recover easily from failures.
Horizontal scaling only works when your API is stateless. Every request should carry all the information needed to process it, without depending on in-memory sessions or server-specific state.
Step 3: Once the API layer is sound, attention must shift to the database.
Because this is where most systems hit their limits. APIs can often handle high request rates, but databases cannot tolerate inefficient queries at scale.
Poor indexing, unbounded queries, or mixing heavy reads and writes in a single datastore can quickly become your worst enemy. To scale safely, queries must be predictable, indexed, and measured.
In many cases, separating read and write workloads or reducing database dependency through smarter access patterns makes a bigger difference than optimizing application code.
Step 4: Caching is one of the most effective tools for reducing load and improving performance.
Not every request needs fresh data, and many responses are identical across users or time windows. By caching these responses at the right layers, you remove the need for unnecessary computation and database traffic.
This helps to reduce latency for users and increases capacity for handling truly dynamic requests. In short, effective caching is intentional, with clear rules around expiration, invalidation, and scope.
Here’s why Rate Limiting is Important for APIs
As traffic grows, protecting the system becomes just as important as serving it. Rate limiting ensures that no single client or integration can overload your API, whether through misuse, bugs, or unexpected retries.
It’s quite clear that without respectable limits, small failures can bring large outages. With limits in place, the system can slow down gracefully instead of collapsing like dominoes.
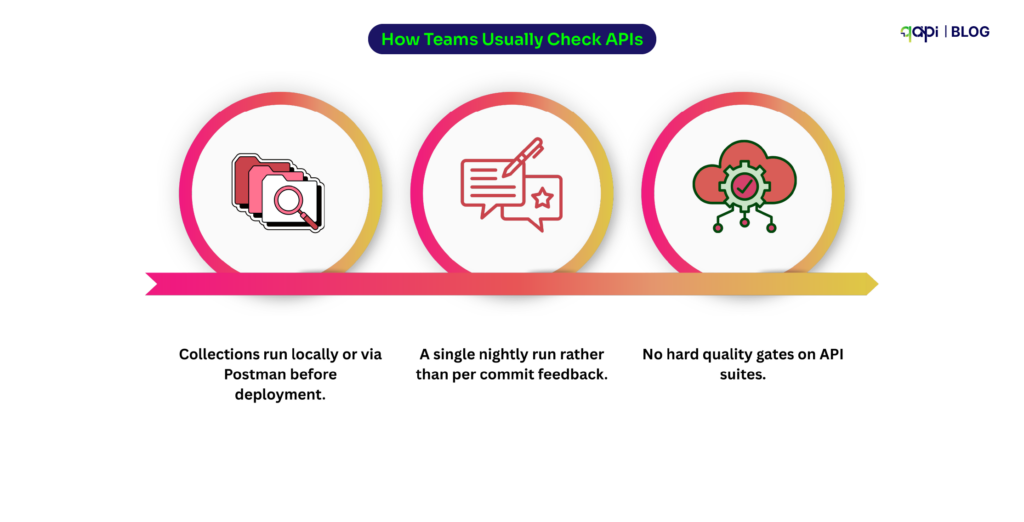
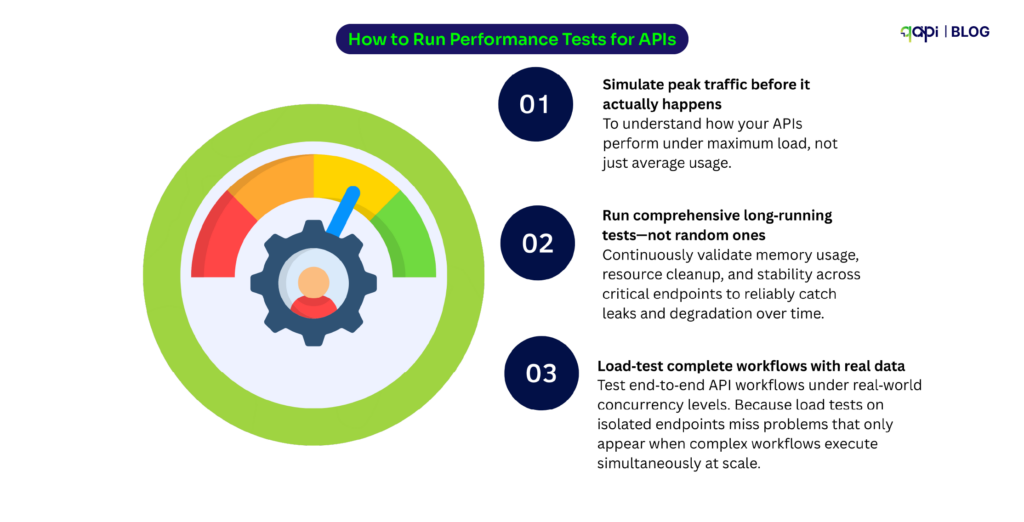
API Testing is where many teams underestimate risk. Because APIs will behave well in development but fail under real-world conditions as local tests lack concurrency, volume, and failure scenarios.
When APIs scale the retries overlap, timeouts compound, and small delays create more issues. This is why scalable systems validate not just correctness, but behavior under load. Performance characteristics, error handling, and edge cases must be understood before users discover them.
Observability ties everything together.
You cannot scale what you cannot see. Tracking latency, error rates, and traffic patterns at the endpoint level allows teams to detect stress before it turns into downtime. More importantly, it helps identify which parts of the system break first under pressure.
When teams rely only on general metrics, failures will feel sudden and mysterious to you. But when visibility is built in, scaling will give you a controlled process rather than the prior.
Ultimately, scaling an API is not a single decision or a one-time optimization. It is the result of strategic architectural choices that prioritize statelessness, ensure performance, and system-wide resilience. Teams that scale successfully do not wait for traffic to expose weaknesses; they design for those weaknesses in advance.
The goal is not to handle a specific number of requests per second. The goal is to build an API that continues to behave predictably as usage grows, complexity increases, and conditions change. When that mindset is in place, scale becomes an engineering problem you can plan for, not a crisis you react to.
HTTP Methods and why you need to know them
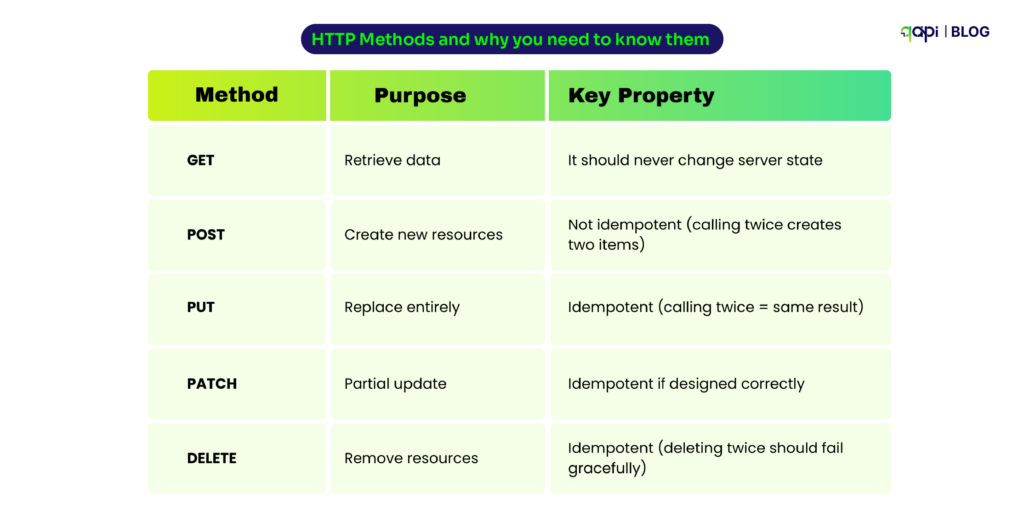
Here’s what trips up even experienced developers, we a similar pattern and listed down some of the major problems that they frequently face:
GET requests with hidden side effects If your GET endpoint is able to logs analytics, updates counters, or does anything beyond returning data, you’ll break caching. So, clients and CDNs expect GET to be safe and repeatable.
POST vs. PUT confusion When clients retry to execute failed POST requests, duplicates are created. PUT is replaces safely. Choosing the wrong method means users accidentally ordering the same item twice.
Non-idempotent DELETE operations If deleting a resource once works but deleting it again returns an error, clients can’t retry safely. Well-designed DELETE operations handle “already gone” gracefully.
The Simple Process that teams should have: Thinking About Retries
Every production incident teaches you the same lesson: network calls fail, and clients retry.
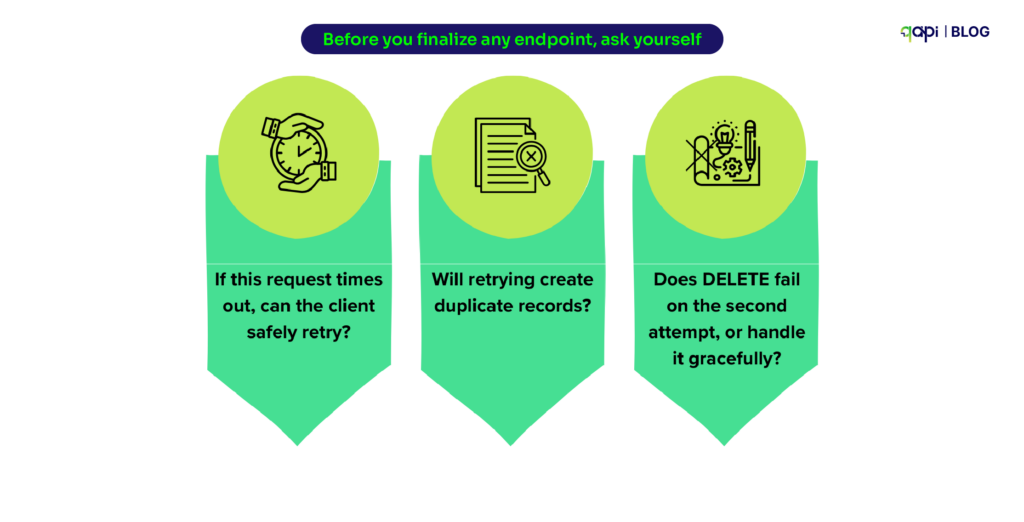
Before you finalize any endpoint, ask yourself:
- If this request times out, can the client safely retry?
- Will retrying create duplicate records?
- Does DELETE fail on the second attempt, or handle it gracefully?
qAPI tip: Send the same POST request twice. If it creates two resources, document that behavior. Your API consumers need to know.
The Mistakes That Cost Production Incidents
Chatty APIs Requiring 10 requests to render one screen. Each round trip will add latency, and the chances of failure increase.
God Endpoints Too much dependency on one endpoint: POST /processEverything. It becomes harder to test APIs and much harder to maintain.
Leaky Abstractions Exposing database JOIN results directly as API responses. Your internal schema becomes a public contract.
Ignoring HTTP Semantics Teams use POST for everything or returning 200 OK with error payloads. This confuses clients and breaks caching.
No Pagination Returning unbounded arrays that crash mobile apps when users scroll.
Tight Coupling Designing APIs around one specific client. When that client changes, your API breaks.
qAPI tip: We recommend that if your tests require a complex multi-step setup, your API design might be the problem. So ensure your so-called “good” APIs are testable.
Now that you know what to do and what not to do, here’s a checklist to keep handy.
Best Practices Checklist for REST APIs




Why REST API Automation, Why Now: The Economic Case
Two hard realities drive the case for automated (API) testing:
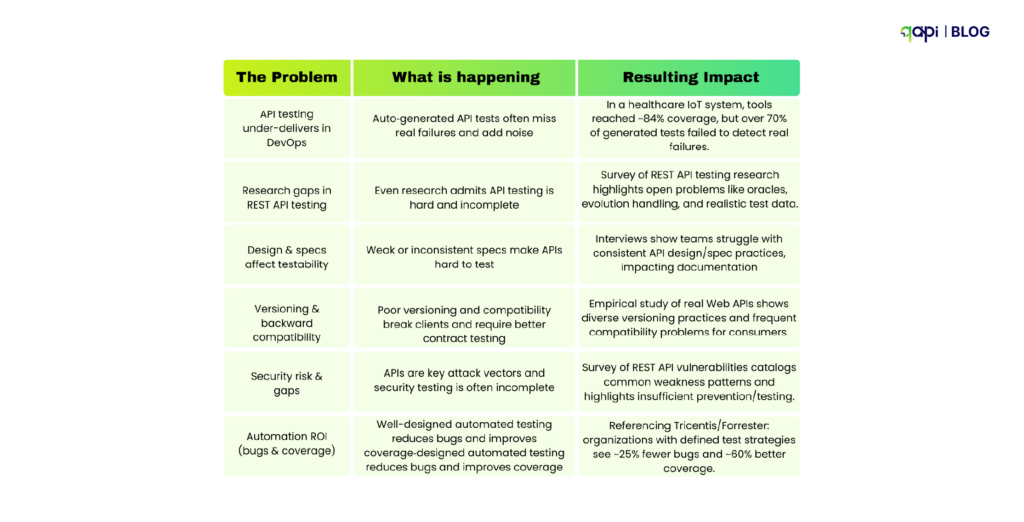
- Downtime is punishingly expensive. Industry analyses put the average cost of IT downtime at $5,600 to ~$9,000 per minute, and regulated verticals can exceed $5M per hour when you factor revenue loss, SLA penalties, and reputational damage. [atlassian.com]
- Defects get exponentially more expensive the later you find them. NIST/IBM research has long shown that finding/fixing defects after release can cost up to 30× more than catching them early—exactly what automated, continuous testing is designed to prevent. [public.dhe.ibm.com]
If your pipelines aren’t automatically validating API behavior at every merge and deploy, you’re effectively accepting a higher probability of costly production incidents.
Automated API testing offers four decisive advantages:
- Speed: API tests run faster (seconds vs. minutes) and integrate earlier in the pipeline, giving developers feedback per commit/PR. Faster feedback shortens lead time and lowers change failure rate—direct DORA wins.
- Stability: API tests don’t break on CSS tweaks or DOM reshuffles; they validate the system’s contract and behavior, not presentation details—reducing false failures.
- Coverage: You can test edge cases and error paths that are hard to reach via UI. With service virtualization, you can also simulate unavailable dependencies to test negative flows and peak loads safely.
- Security: API tests can continuously validate auth, rate limits, data exposure, and other OWASP API risks—a critical gap when most organizations lack full inventories yet face rising attack traffic.
The Hidden Tax You Can Eliminate: Endless Test Maintenance
Many organizations have/are “automate everything” and ended up with the maintenance spiral: brittle assertions, hardcoded payloads, failing tests after harmless changes. The result is toil: engineers stop trusting tests, and CI becomes noisy.
What actually breaks the cycle:
- Contractaware assertions: Tie tests to API intent (schema/semantics), not to fragile field order or presentation quirks—so additive, backwardcompatible changes don’t fail.
- Changeaware test selection: Detect what changed (new field vs. contract break) and run only impacted tests; surface remediation context in PRs before a full CI redout. (This is the same “shiftleft” logic that improves DORA throughput and stability.)
- Behaviorlearning: Use real execution data to learn valid variability ranges and common call patterns, so your suite flags true regressions instead of benign drift (critical as AIdriven API traffic increases).
When teams adopt these patterns, maintenance drops, signaltonoise improves, and developers treat CI failures as actionable reality, not background hum.
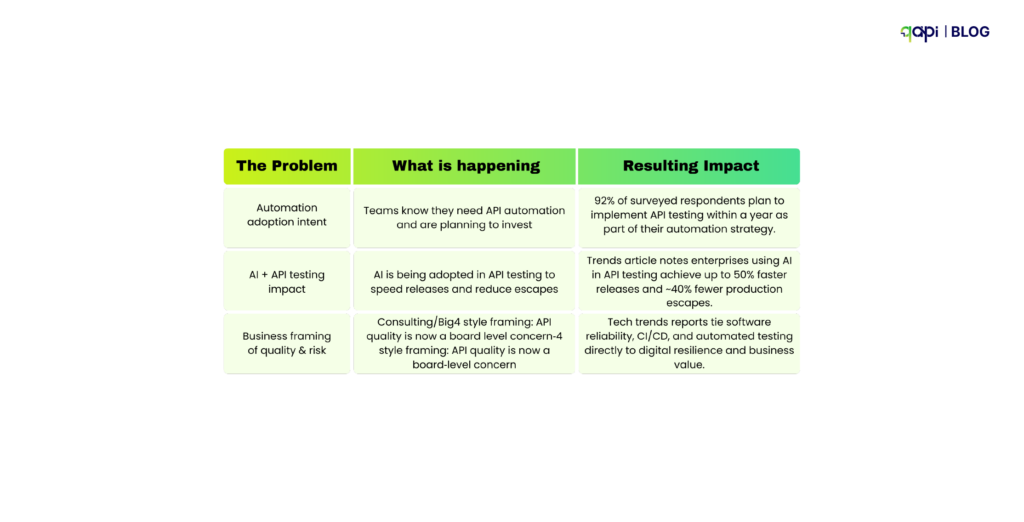
Some Predictions: The Next 24 Months of Automated API Testing
- APIfirst → AIfirst APIs. As agents and copilots become consumers of APIs, the volume, frequency, and variability of calls will grow—change aware and behavior learning testing will go from “its nice” to groundbreaking.
- From tools to platforms. Testing will integrate tightly with API catalogs, gateways, and observability—blurring the line between design time testing, preprod checks, and runtime conformance. Organizations that centralize inventory and governance will have outsized reliability gains, addressing the full inventory gap.
- Safety and speed converge. High performers will continue proving there’s no tradeoff between speed and quality (DORA). Expect leaders to emphasize test impact analysis, runtime informed tests, and security validations in CI to keep change failure rates low while increasing deployment frequency.
- Ops economics will rule decisions. With downtime costs at $5.6k–$9k/min and remediation at ~$591k per incident, CFOs will favor investments that demonstrably reduce incidents and MTTR—and automated API testing tied to DORA metrics will be central to that argument.
Final Word
The software market is building on a simple truth: APIs are where business happens—and automated API testing is how you protect that business while moving faster. The data is unambiguous: API adoption and AIdriven traffic are rising, visibility gaps persist, incidents are frequent and expensive, and high performers prove that speed and stability can (and should) rise together.
If you modernize testing around contracts, change awareness, behavior learning, and CI/CD guardrails, you’ll break the maintenance spiral, reduce risk, and ship confident changes continuously. That’s the future customers (and CFOs) will reward. And you can do all that and still some more with ease on qAPI.