End-to-End API testing is a phrase or a dream that developers and testers type into search engines like Google or ChatGPT to find a tool or a service that can deliver that.
Most teams today juggle multiple tools—Postman for functional checks, Swagger or OpenAPI for contracts, custom scripts for performance, and other utilities for virtual user simulation.
The problem? Switching between tools is slowing you down, increasing maintenance overhead, and leaving gaps in coverage. Hard to get around it?
Now, imagine having everything in one platform: writing tests, running functional and performance checks, simulating complex user workflows, handling asynchronous calls, and managing dependencies—all without stitching together a dozen tools.
Whether you’re debugging a critical payment flow, scaling a SaaS backend, or validating a complex microservices chain, the goal is simple: make your APIs unbreakable, reliable, and production-ready—every single time.
In this guide, we’ll break down the core concepts, best practices, and essential features you need to build a robust end-to-end API testing strategy that actually works in 2025 and 2026.
1️⃣ What is End-to-End API Testing?
End-to-end API testing is the process of validating the complete flow of an API-driven application, from start to finish, without touching the UI. In simple terms, it connects multiple API calls—think sending a request, processing data through services, and verifying the final response—it ensures that the API responds at each stage.
This is precisely what qAPI offers; it’s the only end-to-end API testing tool that’s capable enough to handle all your API testing needs in one place.
E2E Testing addresses broader issues, such as data consistency across chains, real-world failures (e.g., timeouts in asynchronous calls), and system-wide reliability. It catches issues that lower-level tests miss, such as a login API followed by a purchase portal, failing due to session mismatches.
2️⃣ What is Covered in End-to-End API Testing
In 2025, trends such as AI-powered automation, shift-left testing, and low-code platforms are making End-to-End (E2E) API testing non-negotiable. With APIs handling real-time data in edge computing and serverless architectures, a single glitch can cascade into outages.
To use an API effectively, you need targeted checks that test the specific aspects of the API you are using. Here are the different types of API tests, along with what you should know about them.
Functional Testing
You must start with functional tests to validate that each API endpoint behaves as intended. It checks status codes, response formats, error handling, and business logic.
• Example: A /login endpoint should return 200 OK with a token when valid credentials are provided, and 401 Unauthorized when they are not.
Contract Testing
In contrast, you ensure that APIs adhere to their agreed-upon specification, typically defined in an OpenAPI or Swagger document. This prevents breaking changes between providers and consumers.
• Example: If the contract specifies that the currency must be in ISO format, responses returning USD instead of $ should fail the test.
Workflow (Process) Testing
Validates that a complete business process works as expected when APIs interact with each other and external systems. Unlike simple end-to-end tests, workflow testing often spans multiple domains, services, and even user roles.
Performance Testing
Finally, the most important of all, the Performance test measures how well APIs perform under different loads and conditions. It checks response times, throughput, scalability, and system stability.
Example: The /checkout endpoint should handle thousands of concurrent requests without exceeding agreed latency thresholds.
All of these major requests can be found in one single cloud tool, so that you don’t have to juggle your API collections from one place to another.
3️⃣ How End-to-End API Testing Works: Core Concepts
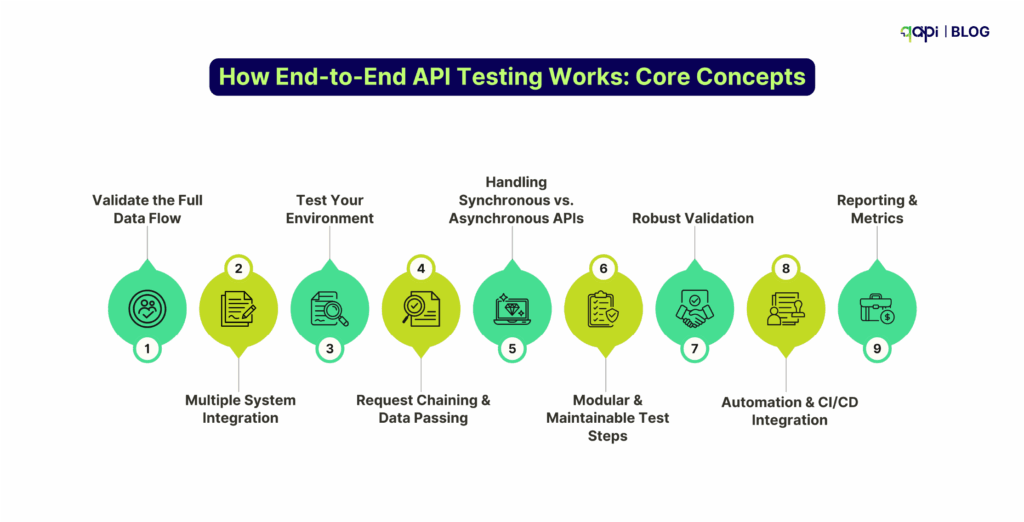
Think of end-to-end API testing as recreating a real user journey—step by step, but at the API layer.
1️⃣Validate the Full Data Flow
Example flow:
• A mobile user logs in → API call to the authentication service
• Their profile data loads → API call to the user service
• They place an order → API calls to the payment gateway and inventory service
• The system responds with an order confirmation
An end-to-end test simulates this chain, making sure each call works individually and that the entire process delivers the right outcome.
2️⃣ Multiple System Integration
E2E tests confirm that all components work together:
• Internal microservices
• Third-party APIs (payments, SMS, email)
• Databases and caching layers
• Message queues and event-driven systems
This builds resilience against failures in external systems and uncovers integration issues early.
3️⃣ Test Your Environment
Tests are only as good as the environment, so start by creating:
• Dedicated environments that mirror production
• Sanitized real-world data
• Matching API versions and configurations
Highly unstable environments will reduce environment-specific failures and improve confidence in results.
4️⃣ Request Chaining & Data Passing
E2E workflows rely on passing data between steps, so take care of:
Request chaining: Use tokens, IDs, or session values returned by one API in subsequent calls.
• Variables and environments: Store reusable data like user IDs, order numbers, or auth tokens for dynamic, realistic tests.
• Reddit insight: Developers often mention that chaining and dynamic data are the trickiest parts of end-to-end (E2E) testing, but they are essential for reliability.
5️⃣Handling Synchronous vs. Asynchronous APIs
Decide, test how you want your APIs to interact in the entire ecosystem
• Synchronous APIs: Immediate responses—simply chain the next request.
• Asynchronous APIs: Background jobs, webhooks, or queues—use polling (asking “is it done yet?”) or callbacks (system signals completion) to verify outcomes.
6️⃣Modular & Maintainable Test Steps
• Break tests into reusable, composable steps
• Keep one assertion per concern
• Use parameterized inputs to cover different data scenarios without bloating the suite
This ensures maintainability, reduces flakiness, and allows teams to expand coverage efficiently.
7️⃣Robust Validation
End-to-end testing goes beyond just checking HTTP responses; it should check:
• Status codes (200, 400, 401, 500, etc.)
• Response body structure and fields
• Database state changes
• External system interactions (emails, logs, notifications)
Also, include edge cases and failure scenarios, such as invalid inputs, network errors, and service outages.
8️⃣Automation & CI/CD Integration
Your plan should be to automate tests for speed and consistency:
• Run tests on every pull request
• Fail fast if workflows break
• Ensure integration of pipelines via GitHub Actions, Jenkins, or GitLab CI
Automation enables the early detection of regressions and facilitates faster delivery cycles.
9️⃣Reporting & Metrics
An effective end-to-end api testing tool should be able to track, summarize, and report the following:
• Test pass/fail rates
• Execution times
• Root cause analysis
• Performance trends
Relying on dashboards and reporting tools (such as Allure, Sentry, and Jira) is no longer necessary, as qAPI provides visibility for both developers and QA teams.
Key Takeaways
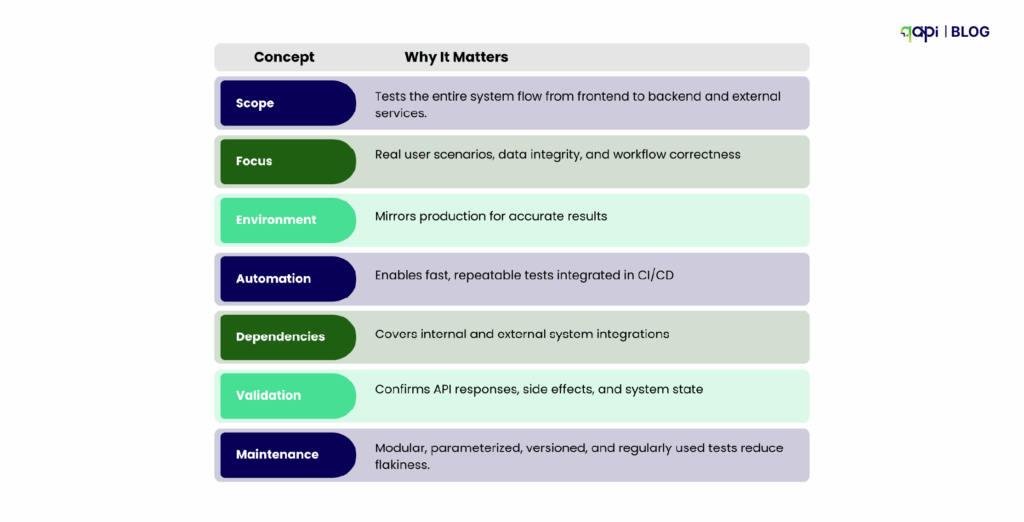
Reddit-inspired insight: Developers frequently note that E2E testing becomes maintainable and actionable only when workflows are modular, parameterized, and versioned, with proper environment setup and realistic test data. Without these, E2E tests often break or provide false confidence.
4️⃣ Preparing for E2E API Testing
Many testers on Reddit stress that setup makes or breaks your test strategy. Without the right environment and data, tests either break constantly or give false confidence.
To start, you’ll need staging environments mirroring production, realistic test data (synthetic or anonymized), and setup scripts for dependencies. qAPI is your best bet for all your needs Before you start punching requests and validating workflows, you need the right strategy. A strong setup will save you from wasting your time. Here are the essentials:
1️⃣Test Environment Setup
• Staging environment → A safe space for production where breaking things won’t affect users.
• Test database → Filled with clean, predictable data you can reset between runs.
• Third-party service mocks → Stand-ins for external systems (like payment gateways) so tests don’t trigger real charges.
2️⃣Test Data Strategy
• Static data → Fixed users, accounts, or products that stay the same across runs for predictability.
• Dynamic data → Freshly generated values (like unique emails or order IDs) to avoid collisions.
• Data cleanup → Reset or clean out records after each run so tests remain reliable.
q tip: Use a dedicated “test tenant” or “test organization” to keep test data completely separate from production data.
3️⃣Dependency Management
APIs rarely work alone. External services—such as payment gateways, third-party APIs, or other systems beyond your control—pose challenges for stable testing. That’s where parametrization comes in.
Instead of hardcoding values or relying on unpredictable responses, qAPI lets you define parameters that make tests flexible, reproducible, and scalable.
Why parametrization matters:
• Create parameterized mock APIs directly from your OpenAPI spec. Pass parameters to generate realistic responses instead of hitting live services—because it’s safer, faster, and cheaper during early testing.
• Define expected outputs through parameters (e.g., always return a valid payment ID) to keep workflows stable and reproducible.
• Find a tool where you can simulate high-volume requests with parameterized mocks, avoiding quotas or per-call charges on external APIs.
With qAPI, you don’t need separate tools for mocks, virtual users, environments, or test data management; you get it all!
To avoid confusion, here’s a simplified strategy for E2E API testing, which begins with planning and prioritization.
• Identify critical workflows: For example, login → order placement → payment → notification.
• Define success criteria: Status codes, JSON fields, latency limits, and business rules.
• Adopt risk-based testing: Cover the most critical and high-risk endpoints first.
• Document workflows: Keep expected behavior, edge cases, and error handling clear for developers and testers.
5️⃣Best Practices and Pro Tips for Effective E2E API Testing
Sustainable E2E testing is more than writing scripts—it’s about modular design, version control, stabilization, and continuous pruning.
Here’s how to develop one step-by-step:
• Define Clear Requirements: Start with well-defined specs using OpenAPI or Swagger. This sets the foundation for contract testing, ensuring producers and consumers agree on requests/responses.
• Adopt a Layered Approach: Combine unit tests for single endpoints, integration for service interactions, and end-to-end for full flows. Prioritize based on risk—focus on high-traffic or critical paths first.
• Incorporate Automation Early: Use AI-powered tools like qAPI to auto-generate tests from specs, covering happy paths, negatives, and edges. Automate in CI/CD to run on every PR for fast feedback.
• Include Non-Functional Testing: Don’t skip load, stress, and security—set SLOs for response times and use fuzzing for robustness.
• Measure and Iterate: Track metrics like coverage percentage, flake rate, and escaped defects. Review quarterly to refine.
This methodology will reduce rework by 60-80%, making your strategy agile and effective.
Documentation Requirements
• Use Standardized Specs: Adopt OpenAPI/Swagger for detailed endpoints, parameters, responses, and examples. This enables the generation of auto-tests and contract validation.
• Include Test Cases: Document happy/negative paths, edge cases, auth flows, and error models. Tools like Postman can embed these in collections for living docs.
• Version Control: Keep docs in the same repo as code—review in PRs to catch drift. Use semantic versioning for APIs to manage changes without breaking tests.
• Security and Compliance Notes: Detail auth (OAuth/JWT), data masking, and standards like OWASP to guide security testing.
• Accessibility for Teams: Make docs collaborative—qAPI’s shared workspaces let developers and testers update in real-time.
In the fresh rollout, qAPI will release the AI summarizer tool, which will help explain the workflows you create. All you have to do is copy the explanation and send it internally, so all your teams are on track and know how the APIs are designed and how data flows across the pipeline.
Test Coverage Optimization
Optimizing coverage means testing smarter, not more—aim for 80-90% coverage in critical areas without overstuffing your test suites. In 2025-26, AI and data-driven methods help maximize this.
Strategies to optimize:
• Risk-Based Prioritization: Focus on business-critical endpoints (e.g., payments) and high-risk scenarios like invalid inputs or rate limits.
• Data-Driven Testing: Parameterize tests with datasets for varied coverage—synthetic data generators in qAPI can handle edges like special characters or nulls without manual effort.
• Performance and Security Inclusion: Cover load thresholds and OWASP checks to ensure non-functional optimization.
This approach enhances reliability while maintaining fast test times, resulting in 60% better bug detection, as observed in real-world cases.
Collaboration Between Testers and Developers
Great API testing thrives on teamwork—breaking silos leads to better quality and faster cycles. In 2025, DevOps and shift-left foster this.
Ways to enhance collab:
• Shared Tools and Workflows: Use qAPI (up to 5 users free) for joint test creation and reviews. Devs write unit tests; testers handle E2E—review together in PRs.
• Contract-First Development: Devs define specs early; testers generate tests from them. This aligns expectations and reduces handoffs.
• Blame-Free Culture: Focus on issues, not people—use retros to improve processes.
Elevate Your API Strategy
The future of software quality is API-first, and organizations that adopt end-to-end testing early gain a decisive advantage.
By now, you know it, and your teams know it.
Let’s start by testing comprehensive workflows, simulating real-world user behavior, and handling dependencies seamlessly. You ensure your APIs are dependable, scalable, and production-ready.
• Refine test coverage across critical workflows and edge cases
• Automate meaningful validations rather than superficial checks
• Monitor real-world performance and adjust tests proactively
Start now: audit your workflows, implement end-to-end testing with qAPI, the only unified platform, and track holistic metrics that capture true API reliability.
Teams that invest in comprehensive E2E testing today will build systems that scale safely, perform consistently, and delight users tomorrow.

