The misalignment between what you intend for your APIs and how they perform is sometimes bigger than you imagine. Have you ever witnessed that? Have you thought why is that way?
Well, the gap starts to widen along the testing and shipping process. APIs that look fine in development often stumble in production—causing downtime, you lose appear fine in development often stumble in production—causing downtime, losing customers, and endless pressure on sales. For QA, it feels like chasing problems that could’ve been prevented. For developers, it’s the frustration of watching good code fail because testing came in too late.
Performance testing is straightforward. It ensures that your APIs are scalable and can handle any amount of traffic and instability thrown towards them.
However, manually testing APIs or generating test cases can be a time-consuming and inefficient process. You’d end up spending more time accessing breakdowns than you would generating them.
That’s why it’s important to simulate users in your API testing process. It ensures your APIs are aligned to your product goals, you know before performance degrades and helps you plan infrastructure needs.
In this blog, we will learn how to test API performance, latency, throughput, and error rates under load. And how you can set your APIs to build scalable and efficient applications.
What is Performance Testing in APIs?
Performance testing for APIs is a process we use to understand how well your API handles load, stress, and various usage patterns. Unlike functional testing, performance testing measures how quickly and how much load your API can handle before it breaks. Such as:
• Response Time – How quickly the API responds to requests
• Throughput – How many requests per second the API can process
• Latency – Time delay between request and first byte of response
• Error Rate – Percentage of failed requests under load
• Resource Utilization – CPU, memory, and database usage during testing.
The following factors help developers and SDETs understand how to build APIs that are more likely to fail. By ensuring the API account well on these aspects, you ensure that your APIs bring the trust you need.
Types of API Performance Testing:
• Load Testing – Normal expected traffic levels
• Stress Testing – Beyond normal capacity to find breaking points
• Spike Testing – Sudden traffic increases (like flash sales)
• Volume Testing – Large amounts of data processing
• Endurance Testing – Sustained load over extended periods
What is the role of Virtual Users in Performance Testing?
Virtual users are simulated users that performance testing tools create to mimic/re-create real user behavior without needing actual people.
How Virtual Users Work:
• Each virtual user executes a script that makes API calls
• They simulate realistic user patterns (login → browse → purchase → logout)
• Multiple virtual users run simultaneously to create a load
• They can simulate different user types, locations, and behaviors
For example, instead of hiring 1,000 people to test your e-commerce API, you create 1,000 virtual users that:
• Log in with different credentials
• Browse products via API calls
• Add items to cart
• Process payments
• Each following realistic timing patterns
Virtual User Benefits:
• Cost Effective – No need to recruit real users for testing
• Scalable – Can simulate thousands or millions of users
• Consistent – Same test patterns every time
• Controllable – Adjust user behavior, timing, and load patterns
• 24/7 Testing – Run performance tests anytime
Virtual User Simulation: Challenges Where Current Tools Fall Short
Realistic User Behavior
• Static scripting limitations – Most tools use fixed scripts that don’t adapt to real user variations and decision-making patterns. All virtual users are designed to act identically but, real users change their minds, make mistakes, retry actions.
• Session complexity gaps – Real users browse, abandon carts, return later – current tools struggle with complex user journey modelling. Virtual users lose context between API calls, unlike real users who maintain browsing state
Authentication and Session Management
• Token refresh complexity – Most tools struggle with realistic JWT token expiration and refresh cycles during long test runs
• Multi-factor authentication simulation – Current tools can’t properly simulate MFA flows that real users experience
Data Management and Variability
• Synthetic data limitations – Test data doesn’t reflect real-world data distributions, edge cases, and anomalies
• Data correlation problems – Virtual users use random data instead of realistic data relationships (user preferences, purchase history)
• Geographic distribution gaps – Most tools don’t simulate realistic global user distribution and network conditions
Technical Infrastructure Limitations
• Resource consumption explosion – Simulation of virtual users consumes significant memory and processing power, causing performance lapses or crashes.
• Network conditions– Tools don’t simulate realistic mobile networks, slow connections, or intermittent connectivity
• Parallel execution problems – Current tools hit hardware limits when simulating thousands of concurrent users
• Increasing cloud costs – Scaling virtual users in cloud environments becomes prohibitively expensive for realistic load testing
These are just challenges that you often face but are avoidable. We’ll explore how smart tactics can put you steps ahead. However, let’s examine how automating API performance tests can simplify the process.
How do I set up virtual users for API performance testing?
qAPI an end-to-end API testing tool offering free Virtual users each month so you can test your APIs for free.
You can also add more virtual users if needed.
Here’s how it works-
Set Up Test Data
• Create varied and realistic test data:
• Use data files (CSV, JSON) for parameterization. Or directly import your API collection.
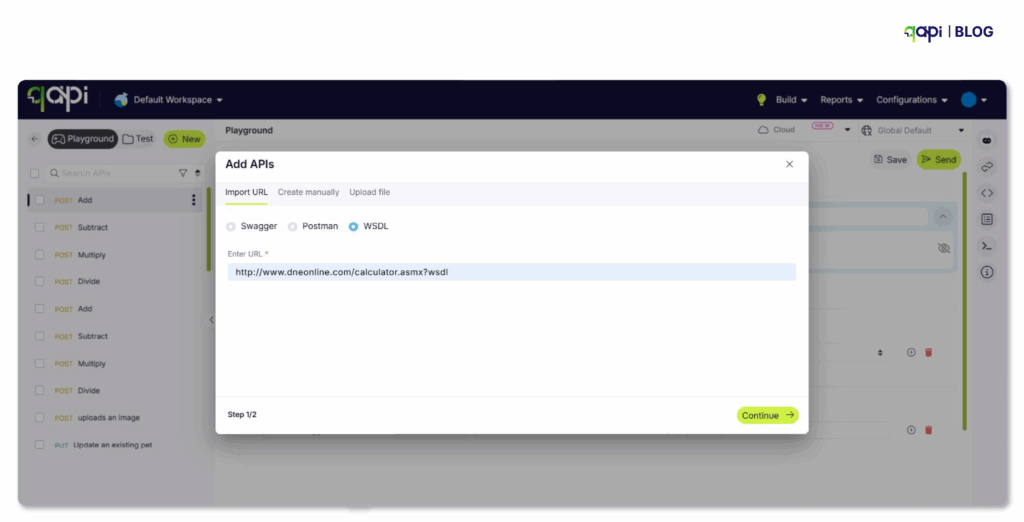
- Include details, edge cases and boundary values
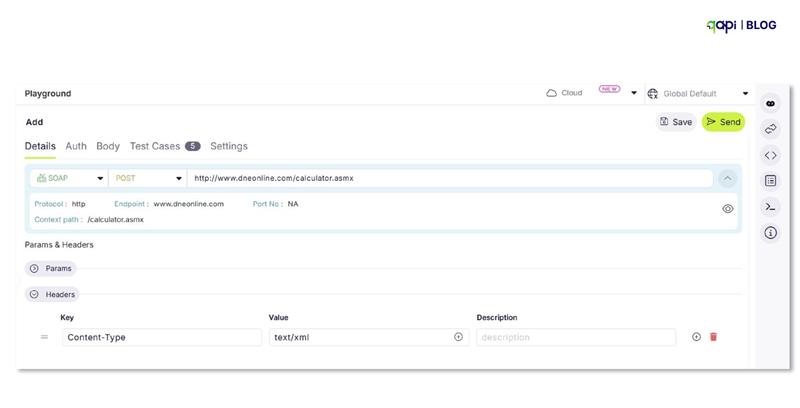
- Add/define test cases
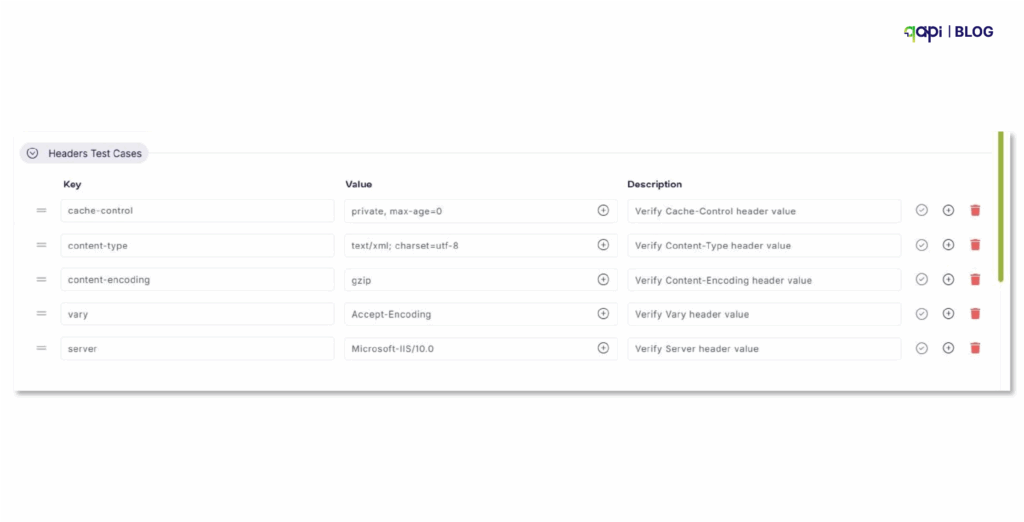
• Define data relationships between requests (if needed)
Configure Monitoring
• Number of virtual users: How many concurrent users to simulate
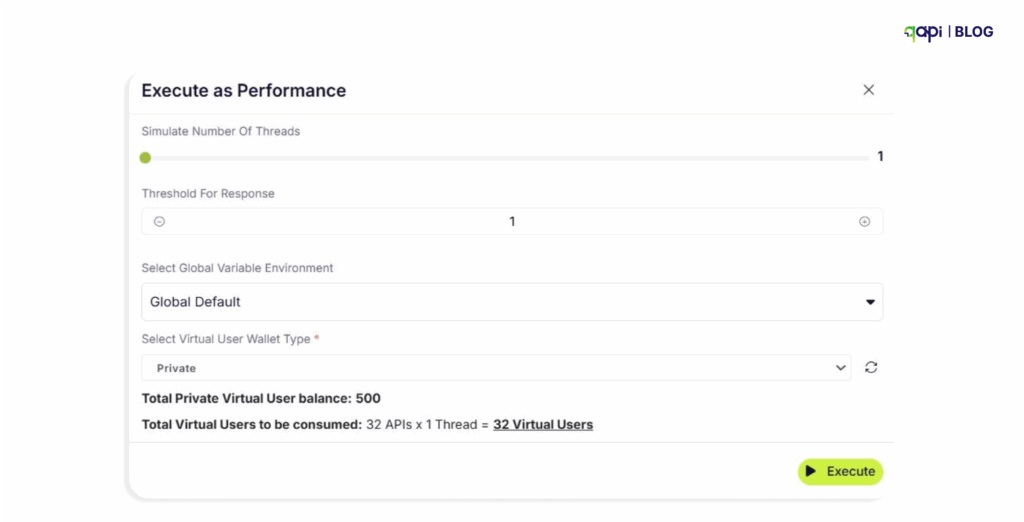
• Ramp-up period: How quickly to start all virtual users
• Loop count: How many times each virtual user should execute the script
• Time between iterations of the script
Execute and Refine
• Monitor for errors or unexpected behavior
• Adjust configuration as needed
• Document any issues or anomalies.
Best Practices for Performance Testing APIs with Virtual Users
Before writing a single test script, establish what you’re trying to accomplish:
• Are you validating that your API can handle expected peak traffic?
• Are you looking to identify breaking points?
• Are you testing a specific endpoint or the entire API ecosystem?
- Based on that, set the following parameters like:
• API must handle 1,000 concurrent users with <2s response time
• System should maintain 99.9% uptime under load
• Error rate must remain below 0.1% during peak load
- Start Small and Scale Gradually
Build your test incrementally:
1️⃣ Baseline test: Verify functionality with a single virtual user
2️⃣ Smoke test: Run with a small number of users (10-50) to ensure basic stability
3️⃣ Load test: Apply expected normal load (what you expect during regular usage)
4️⃣ Stress test: Push beyond normal load to find breaking points
- Test in Production-Like Environments
Your test environment should mirror production as closely as possible:
• Match hardware specifications
• Replicate network configurations
• Use similar database sizes and configurations
• Ensure monitoring and logging match production
4. Run Multiple Test Cycles
Performance testing isn’t a one-time activity:
• Run tests at different times of day
• Test after every major code deployment
• Re-test after infrastructure changes
• Create a performance baseline and track against it
5. Consider Security Implications
When load testing APIs:
• Use test credentials that have appropriate permissions
• Avoid generating real user data
• Ensure you’re not exposing sensitive information in test scripts
• Consider rate limiting and how your API handles abuse scenarios
These steps help ensure your API scales reliably without overcomplicating the process.
Metrics to Monitor During API Performance Tests
Focus on key metrics that reveal how your API performs under load. Monitor these in real-time:
– Response Time: Measures how long the API takes to reply (aim for under 200-500ms for most cases).
– Throughput/Requests Per Second (RPS): Tracks how many requests the API handles per unit of time.
– Error Rate: Percentage of failed requests (e.g., 4xx/5xx errors); keep it below 1% for reliability.
– CPU and Memory Usage: Monitors server resource consumption to spot overloads.
– Latency: Time from request to first response byte; critical for user experience.
How to Analyze the Results of API Performance Tests
Follow these clear steps:
Compare against benchmarks: Check if metrics like response time meet your predefined thresholds (e.g., avg < 300ms); flag deviations.
Review trends and graphs: Use visualizations to spot patterns, such as rising errors as the load increases, or percentiles (e.g., p90 for 90% of responses).
Identify problems: Look for high CPU usage or slow queries causing delays; correlate metrics (e.g., high latency with error spikes).
Iterate and optimize: Retest after fixes, focusing on improvements like reduced response times, to validate changes.
How Performance testing ensures your APIs are scalable and dependable
By simulating VUs, you predict failures, optimize resources, and maintain 99.9% uptime—reducing outages by up to 50% in real cases. In 2025, with API security and performance trends surging (CAGR 32.8% for security testing), tools like qAPI can make this accessible, by cutting costs and boosting confidence.
Conclusion: Level Up with qAPI
Performance testing with VUs transforms APIs from fragile to fortress-like. qAPI’s codeless approach addresses traditional pain points, enabling faster and more realistic tests. Ready to optimize? Sign up for free VUs at qAPI and test today. See the difference for yourself.

